Beyond the Road: The Second Life of EV Batteries Transforming Energy Storage

Harshit Mittal
2 November 2024
Living in a world that’s gearing up through technology, electric vehicles mark one of the most important breakups in our journey towards sustainability and a future genuinely based on clean energy. As we celebrate the promise of these quiet pioneers, we can’t help but ask ourselves the far more profound question of what happens when these vehicles finally reach the end of their life cycle batteries? The rebirth of the EV battery is a very interesting story, almost in terms of a philosophical quest for renewal.
The Life of a Battery: An Exploration into Mortality and New Purpose
It starts with the mining, extraction, and refinement of the raw metals that make up the EV batteries, such as lithium, cobalt, and nickel. These are not mere building blocks; they are one of the critical elements in running electric vehicles and the green movement, storing and releasing energy. These metals are then combined to make cathode and anode materials. These electrodes form the core components of lithium-ion cells, which are assembled into battery modules and packs. As time passes, of course, all batteries start to gradually lose their efficiency and will reach a point where they are no longer able to meet the demands that an electric vehicle will place upon them.
This is the point at which some sort of crossroads is reached: do we simply junk such batteries, or can we somehow give them a new, extended life?
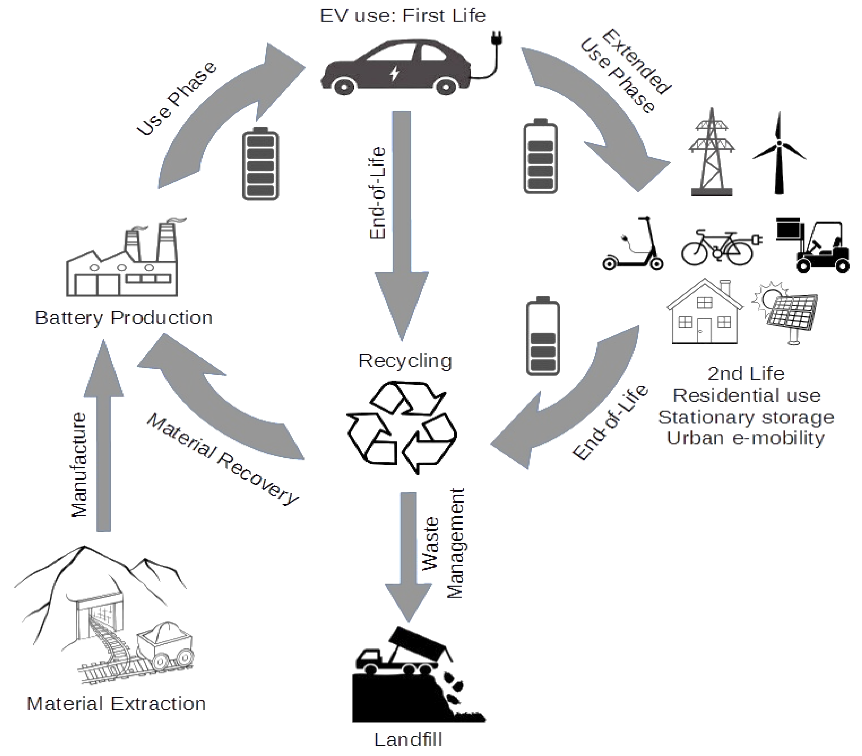
The choice is not only practical; it carries the onus of philosophical sustainability. And in that realization, even when the battery has reached the end of its original usefulness, renewal has beauty in itself, an opportunity to take on another life. The outlook changes the batteries’ end into the beginning of something else and reinforces this reality: resources, which once used, don’t have to go to waste.
Recycling and Reuse of Waste to New Potential
The end of EV battery life can be molded into a new beginning. The used batteries can be recycled through advanced recycling processes into new resources, rebounding for reuse in the making of further innovations and applications. Recycling is a bit like alchemy: it takes something seemingly spent of its life force and turns it into the very building blocks for something new, useful, and full of life.
1. Pyrometallurgy and hydrometallurgy are two of the main recycling techniques through which the batteries undergo heavy processes for retrieving valuable metals. On one hand, pyrometallurgy involves heating up the battery at an extremely high temperature, while hydrometallurgy deals with solutions of various types in order to extract metals. These are methods by which everything that is no longer useful is stripped away, leaving only the valuable parts able to be re-refined and re-introduced into the supply chain. This demonstrates the circle of life and death, whereby the annihilation of an old form can give rise to a new one, much like the phoenix rising from its own ashes. At present, only about 5% of lithium-ion batteries are recycled, but with better technologies for recycling in the pipeline, that percentage is assuredly destined to increase.
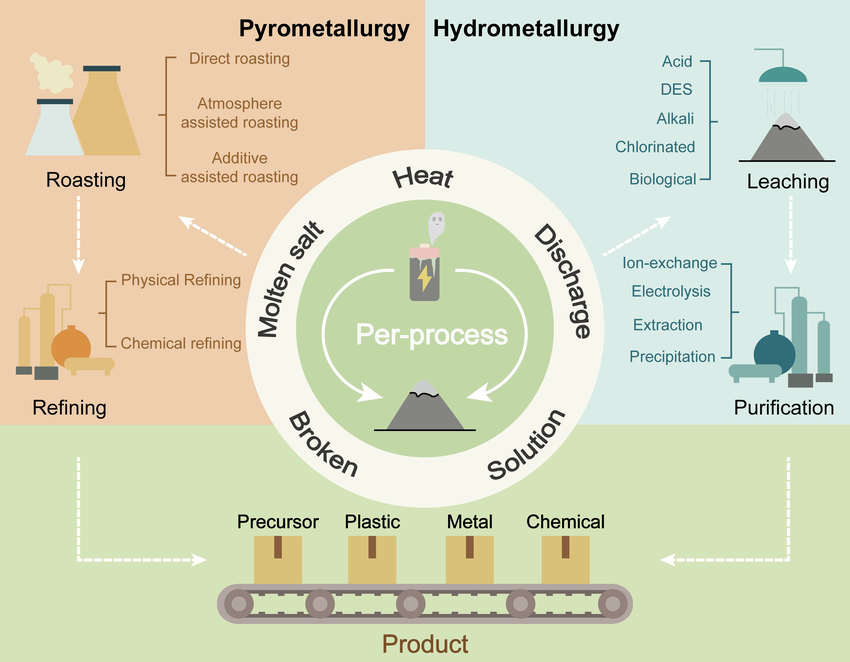
2. Direct Recycling: Unlike pyrometallurgy and hydrometallurgy, in direct recycling, the original structure of the battery remains intact for a large part. Instead of breaking basic metals in a battery, the direct recycling process reconfigures the old battery into a new one or one that could be repurposed for other energy storage applications. The concept is based on circularity, wherein a product could be kept in some kind of loop within which the usage and reuse of a product happens, thereby reducing waste and prolonging the utility of its parts. Up to 70% of a battery’s materials can be recovered through direct recycling in this ideal recycling scenario and given another life with very little loss.
A Future of Sustainable Practice:
The recycling of EV batteries is much more than an exercise of how to deal with waste; it is a paradigm shift toward holistic sustainability, where an “end-of-life” product opens new frontiers of growth and innovation. Our recycling and reusing processes of such batteries show our commitment toward a world of respected and reused resources, bringing us closer to a truly circular economy where nothing goes to waste. It is crucial that the world realize the potential this revolutionary idea has and the astronomical changes it brings along with it. This concept of “rebirthing” just MIGHT be what the world needed to solve the looming global threats of clean energy and resource scarcity all the way to economic stability and growth.
Do refer to these links for more information:




Leave a Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.